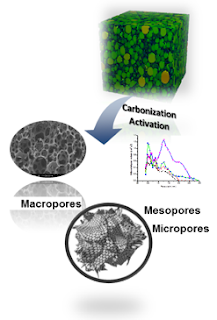
Phenol-urea-formaldehyde (PUF) organic foam were used as precusors for the new monolithic nitrogen-containing microporous cellular activated carbons production. Carbonization and CO2 activation were used to prepare this novel monolithic nitrogen-containing activated carbon foam with both interconnected macroporous and micro/meso- porosity structures from the developed PUF organic foam. The macroporosity corresponded to the connected network of cells with diameters ranging from 100 to 600 µm, and the pinholes in the cell walls had diameters ranging from 1 to 2 µm. The micro/mesoporosity is located at the inner surface of the cells. They can be used just like the classic activated carbon as an adsorbent, catalyst support, energy storage and biological material in various industries, but higher adsorption kinetics. Credit: World Scientific Publishing
Topics: Biology, Biochemistry, Biotechnology, Research
Researchers have developed monolithic, nitrogen-containing, microporous, cellular-activated carbon from phenol-urea-formaldehyde (PUF) organic foam for CO2 and H2 adsorption. The macroporosity corresponded to the connected network of cells with diameters ranging from 100 to 600 μm, and the pinholes in the cell walls had diameters ranging from 1 to 2 μm. The micro/mesoporosity is located at the inner surface of the cells.
Phys.org: Researchers produced nitrogen-doped, cellular-structure-activated carbon
More information: Weigang Zhao et al, Preparation and Characterization of Nitrogen-Containing Cellular Activated Carbon for CO and H Adsorption, Nano (2016). DOI: 10.1142/S1793292017500072
Comments