 |
| Source: NOAA's El Niño Page |
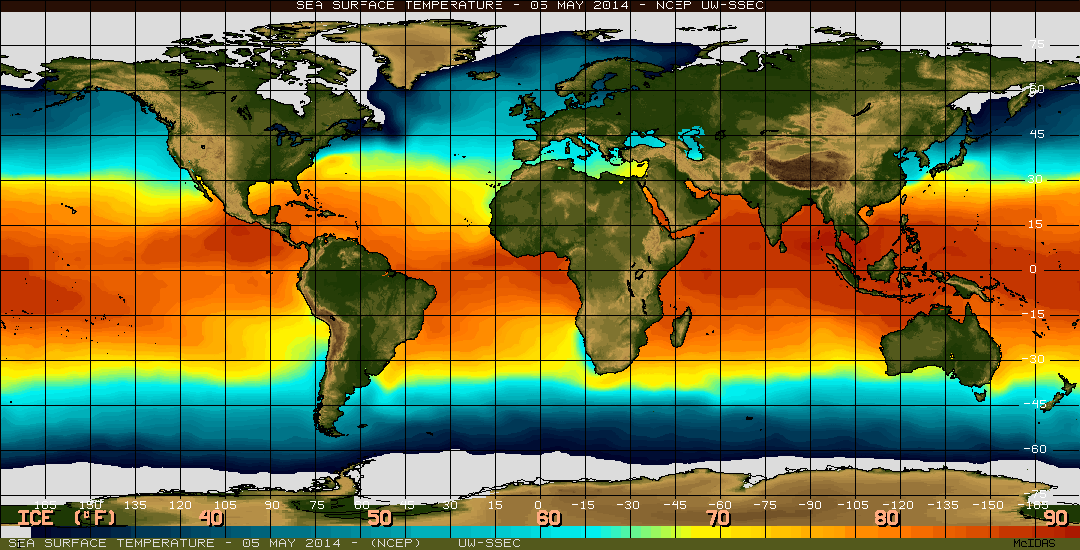
The El Niño / La Niña climate pattern that alternately warms and cools the eastern tropical Pacific is the 800-pound gorilla of Earth’s climate system. On a global scale, no other single phenomenon has a greater influence on whether a year will be warmer, cooler, wetter, or drier than average. Naturally, then, the ears of seasonal forecasters and natural resource managers around the world perked up back in early March when NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center issued an “El Niño Watch.”
The “watch” means that oceanic and atmospheric conditions in the tropical Pacific Ocean are favorable for the development of El Niño within the next six months. These maps reveal one of the most significant of those favorable signs: a deep pool of warm water sliding eastward along the equator since late January.
As the warm surface water is pushed westward by the prevailing winds, cool water from deeper in the ocean rises to the surface near South America. This temperature gradient—warm waters around Indonesia and cooler waters off South America—lasts only as long as the easterly winds are blowing.
If those winds go slack or reverse direction in the western Pacific, the warm pool of water around Indonesia is released and begins a slow slosh back toward South America. The slosh is called a Kelvin wave. If the Kelvin wave has a strong impact on the surface waters in the central and eastern Pacific, then it can help change the atmospheric circulation and trigger a cascade of climatic side effects that reverberate across the globe.
Climate.gov: Slow slosh of warm water across Pacific hints El Niño is brewing
Huffington Post: Climate Change Is Already Here
NOAA's El Niño Page
Comments